In this article, we will see how to enable Enterprise SSO login (based on the SAML single sign-on protocol) using Okta for your Next.js app and relay role-based access directly from the Identity Provider to Cerbos.
We'll be using BoxyHQ's open-source Enterprise SSO solution (called SAML Jackson) to interface with Okta. We'll use the principle of minimal UI and include only the necessary interface in our example application.
Introduction to SAML single sign-on
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) was designed for traditional web applications in the early 2000s. The goal was to provide a seamless user experience for applications by federating authentication to an IdP.
As a result, applications no longer had to maintain identities for users. All they had to do was to redirect the browser to the IdP which would then authenticate the user and return an assertion about the logged-in user.
This assertion in effect was a token, asserting to the app that the user authenticated at the IdP and the assertion is valid for the set period contained within it. You can read more about SAML and other SSO protocols here.
SAML continues to be a very popular choice of protocol when there's a need to provide a single sign-on (SSO) experience for an enterprise application. Microsoft has great resources explaining SAML authentication and SAML at a deeper level.
Benefits of using SAML
Increased Security
SAML is at its heart a security standard and as it provides a single point of authentication that takes place in a secure environment it adds an extra layer of security to your service that most enterprise customers will ask for.
Improved user experience
As a user, SAML is very simple and pleasant to use as you only have to log in once and then you can access all your external services on a dashboard with a single click. This saves the user time and makes their overall experience of your product better.
Reduces cost
Without SAML you have to maintain account information across multiple services but when you use SAML this is all managed by the IdP.
Introduction to BoxyHQ
BoxyHQ implements and maintains an open-source project that handles all the service provider functionality for implementing SAML, hiding away all the complexity you read about above behind the more popular and well-understood OAuth 2.0 protocol.
Introduction to Cerbos
Cerbos is the open-core, language-agnostic, scalable authorization solution that makes user permissions and authorization simple to implement and manage by writing context-aware access control policies for your application resources.
In this tutorial, we are using BoxyHQ as the service provider layer between our example Next.js application and Okta as the Identity Provider to showcase the benefits of syncing roles and permissions during SSO login.
Overview of the example app
The example app is a simple Next.js app that uses SAML Jackson for SAML SSO authentication and Cerbos for authorization.
The app has two pages:
/- Display the authenticated user's profile and authorization decisions returned by Cerbos API./saml-connection- Update the SAML connection details.
The example app runs on port 3000. SAML Jackson and Cerbos are running on ports 5225 and 3593 respectively within Docker containers.
You are free to use cloud versions of Cerbos, the instructions for those wouldn’t change a lot but have been avoided in this article to keep it short.
The example app is configured to work with 2 roles: app-admin and app-user.
The
app-adminrole has access to all resources.The
app-userrole has access to resources only the user owns.
Take a look at the cerbos/policies/contact.yaml file to see how the policies are defined for the example app. You can try changing the policies and see how the authorization decisions change in the app.
The following diagram shows the architecture of the example app.
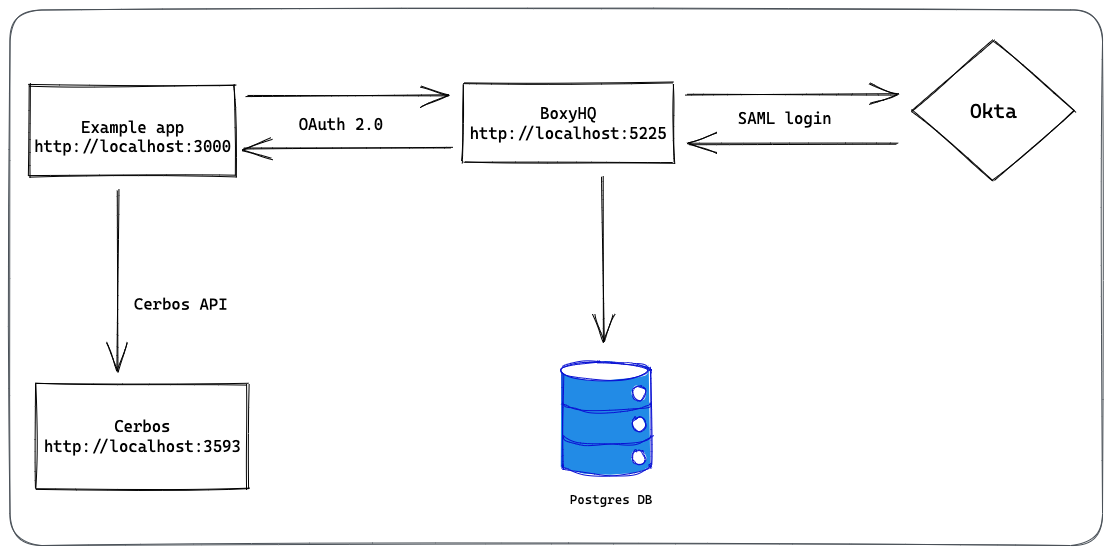
1. Setup the example app
Clone the example app repository:
git clone https://github.com/boxyhq/jackson-cerbos
Navigate to the example app directory and run npm install to install the dependencies.
cd jackson-cerbos
npm install
If you navigate to http://localhost:3000 on your browser, you should see the following page.
This would mean that the example app is running successfully and you can now proceed to the next step.
The README file repository has all details about the example app. You can refer to it if you have anything unclear in this article.
2. Setup SAML App in Okta
The next step is to set up a SAML app in Okta. If you don't have an Okta account, you can create a free developer account https://developer.okta.com/signup/.
Alternatively, you can also use other SAML IdPs like Azure AD, OneLogin, Auth0, etc. The steps for those would be similar to the ones for Okta.
In this article, we will use Okta as the IdP.
If you are unfamiliar with creating a SAML app in Okta, you can follow the instructions here.
You will want to use the Assertion Consumer Service URL and Entity ID from http://localhost:5225/.well-known/saml-configuration.
Do not worry about the roles attribute yet, we’ll configure that in a later step once we have ensured the SSO login flow works correctly.
Next, download the SAML Metadata XML file from the Okta app. You will need this file in the next step.
3. Create a SAML connection in SAML Jackson
Now that we have the SAML app setup in Okta, we need to create a SAML connection in SAML Jackson.
Navigate to http://localhost:3000/saml-connection on your browser and paste the contents of the SAML Metadata XML file you downloaded in the previous step in the XML Metadata field. Click on Create SAML Connection to create the SAML connection.
If you see the status SAML SSO Enabled on the page, it means that the SAML connection was created successfully.
4. Login with SAML SSO
Now that we have the SAML connection setup, we can try logging in with SAML SSO.
Navigate to http://localhost:3000/login on your browser, enter the email address and click on Continue with SAML SSO.
You will be redirected to the Okta login page. Enter the credentials and click on Sign In.
You will be redirected back to the home page of the example app and you should see the Profile of the authenticated user.
This means that you have successfully logged in with SAML SSO.
Since we haven't configured the roles attribute yet, all the users will be assigned the app-user role by default.
5. Configure the groups attribute in Okta App
Now that we have ensured that the SSO login flow works correctly, we can configure the groups attribute in Okta.
Groups attribute allows you to map the groups in your identity provider to the roles in your application.
Create a group in Okta
First, we need to create a group in Okta. Navigate to the Directory > Groups from the left navigation menu.
Click on Add group and enter the group name and description (optional)
Next create two new groups: app-admin and app-user.
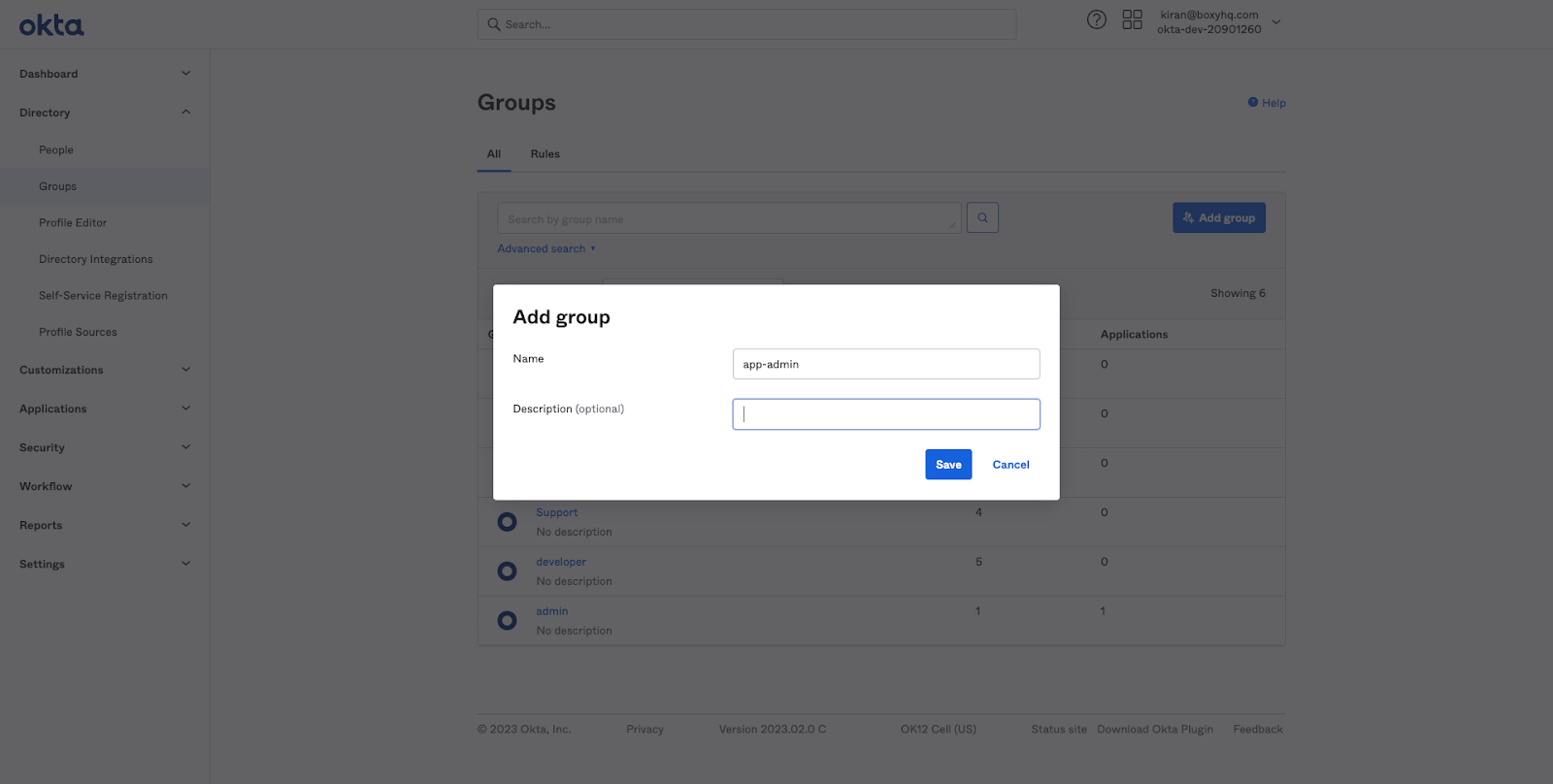
After creating the groups, you will see the groups listed in the Groups page.
Next we need to add the users to the groups. Navigate to the group you just created and click on the People tab.
Click on the Assign people button and assign the users you want to add to the group.
Repeat the same steps for the second group.Configure the groups attribute in Okta
Now that we have created the groups in Okta, we need to configure the groups attribute in Okta.
Navigate to the SAML Settings tab in the Okta app and click on Edit.
Now click on the Configure SAML tab and scroll down to the Group Attribute Statements section.
Click on Add Another and enter the following values
Name: groups
Name format: Unspecified
Filter: Starts with app-
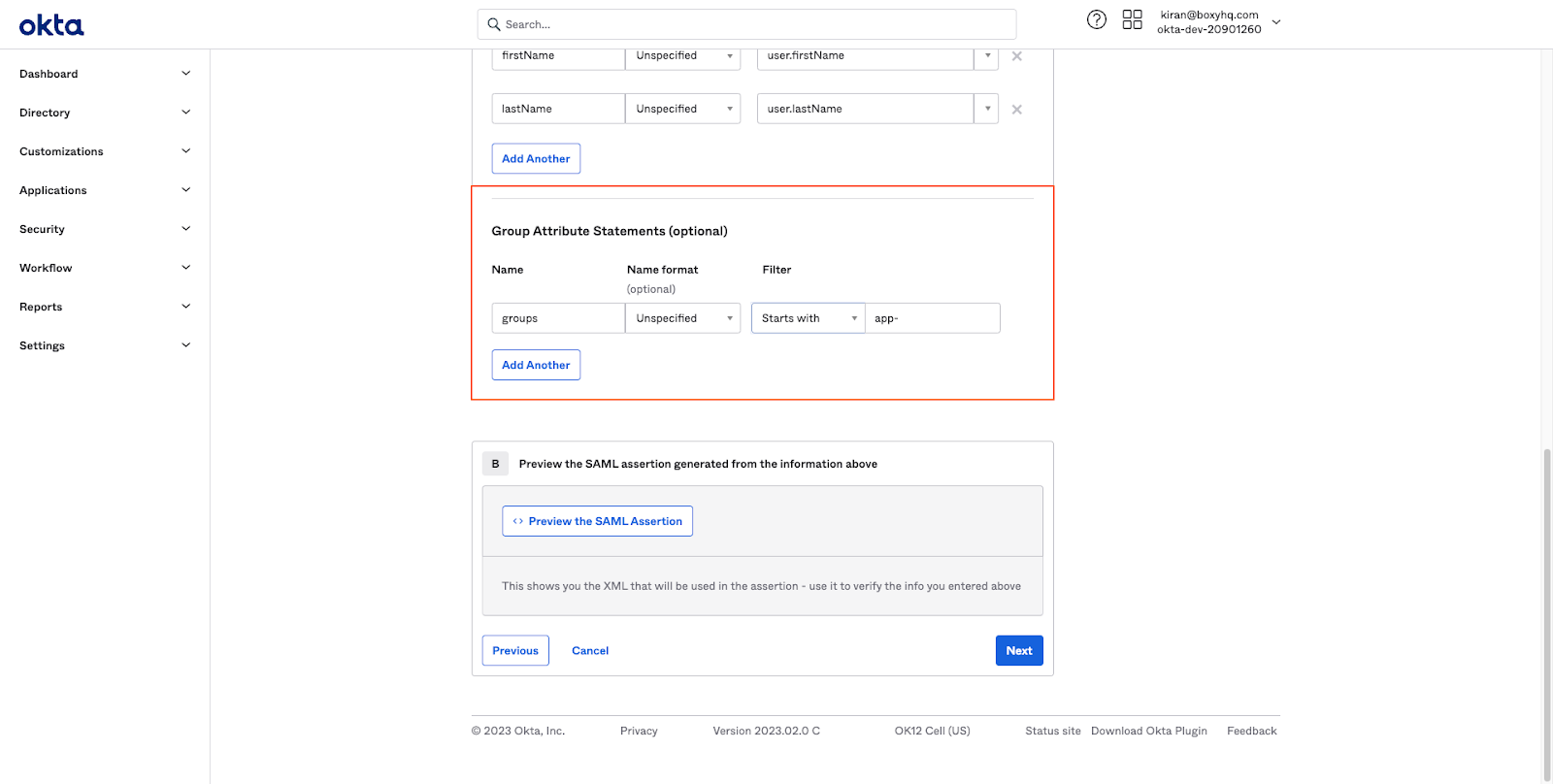
Note the app- prefix in the filter. This will ensure that only the groups that start with app- are returned in the SAML response from Okta. So if you have other groups in Okta, they will not be returned in the SAML response. This is useful if you want to map only a subset of the groups in Okta to the roles in your application.
There are also other filter options available in the Group Attribute Statements section. You can read more about them in the Okta documentation.
6. Test the authorization
Now that we have configured the group attribute, we can test the authorization.
Navigate to http://localhost:3000 on your browser and click the Sign Out button.
Let's try logging in with a user that has the app-admin role.
You will be redirected to the Okta login page. Enter the credentials and click on Sign In.
You will be redirected back to the home page of the example app and you should see the Profile of the authenticated user.
Access API authorized by Cerbos
In the Access API authorized by Cerbos section, we've added a table to display Cerbos authorization decisions for the authenticated user for the resources in the example app.
Here is the overview of the policies defined in the cerbos/policies/contact.yaml file.
A user with the app-admin role can perform all actions on all resources.
A user with the app-user role can perform read and update actions on resources they own.
resourcePolicy:
version: default
resource: contact
rules:
- actions: ['read', 'create', 'update', 'delete']
effect: EFFECT_ALLOW
roles:
- app-admin
- actions: ['read', 'update']
effect: EFFECT_ALLOW
roles:
- app-user
condition:
match:
expr: request.resource.attr.author == request.principal.id
Guarded Routes
In the Guarded Routes section at the bottom of the page, we've added 3 routes to showcase how Cerbos can be used to guard routes in your application.
Route the Admin user role can access: Can be accessed by the user with the app-admin role.
Route the User and Admin user roles can access: Can be accessed by the user with the app-user or app-admin role.
Route the User does not have access to: Can be accessed by the user who owns the resource.
Closing thoughts
In this article, we have seen how to integrate SAML SSO with Jackson and Cerbos. We have implemented authentication and authorization using SAML SSO, Jackson and Cerbos.
This opens up whole new possibilities for enterprise apps using Jackson and Cerbos. I’d love to hear of all the cool apps and features you are going to build, please reach out to Jackson or Cerbos if you found this article useful.
Access the source code for this article here: https://github.com/boxyhq/jackson-cerbos
Learn More
To learn more about SAML Jackson and Cerbos, take a look at the following resources:
